The Common Vein Copyright 2010
Introduction
The prostate has been likened to many structures including a cone, a chestnut, a walnut and a heart.
In the A-P projection it is seen cone shaped organ with apex directed inferiorly and base in contact with the bladder superiorly.
|
Heart Shape or Chestnut or Cone Shaped Common Descriptors of the Prostate |
|
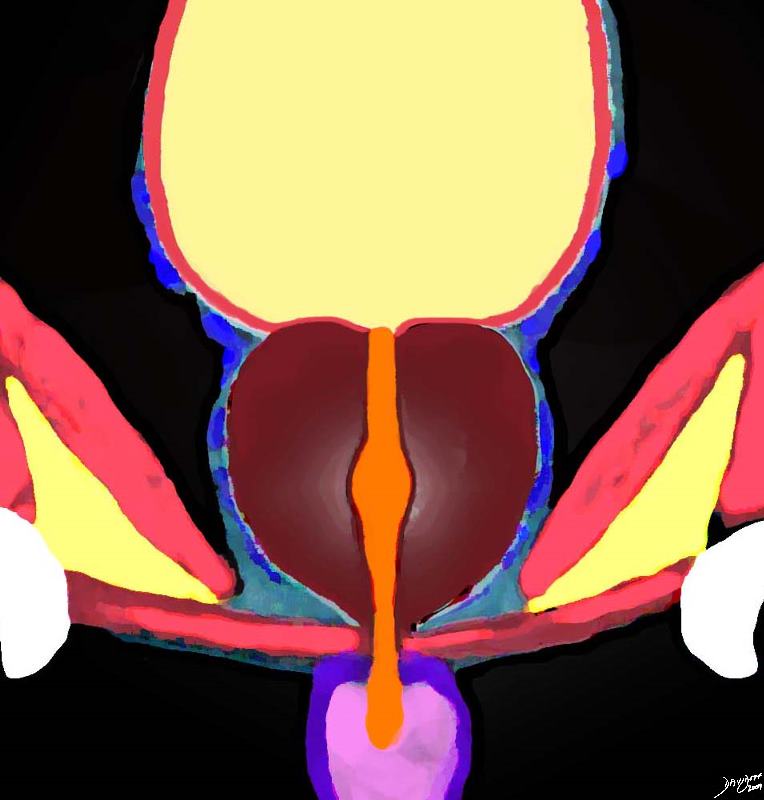
The diagram reflects a normal chestnut shape of the prostate (maroon overlay) seen in the coronal plane. It could also be seen as a heart, a top, a cone, or an acorn. Image Courtesy Ashley Davidoff Copyright 2010 99651b07.8s |
The prostate has anterior, posterior, and lateral surfaces. The anterior surface is rounded, the posterior surface is slightly flattened and the lateral surfaces rounded as well. This shape fits quite accurately with the chestnut as well.
|
The Shape of the Chestnut and The Shape of the Prostate |
|
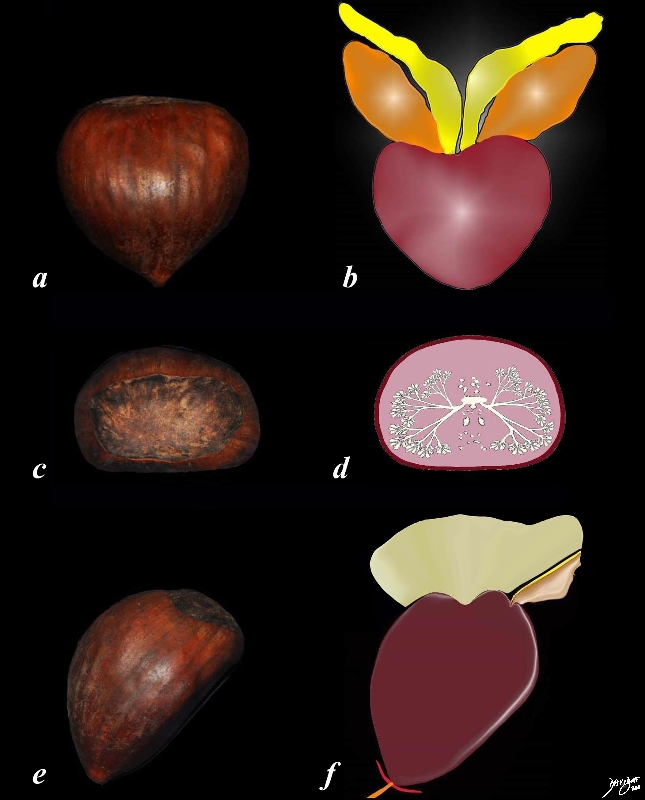
The diagram depicts the chestnut and correlative artistic renderings in the A-P (a,b), transverse (c,d) and sagittal projections (e,f). The rounded anterior and lateral borders and flattened posterior border fit perfectly with the shape of the chestnut, and the even the heart shape in the frontal projection is also the shape of the chestnut. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2011 99662c04L.8s |
In the transverse dimension the prostate is seen at some levels as heart shaped.
|
Heart Shaped in the Transverse Plane T1 Weighted MRI |
|
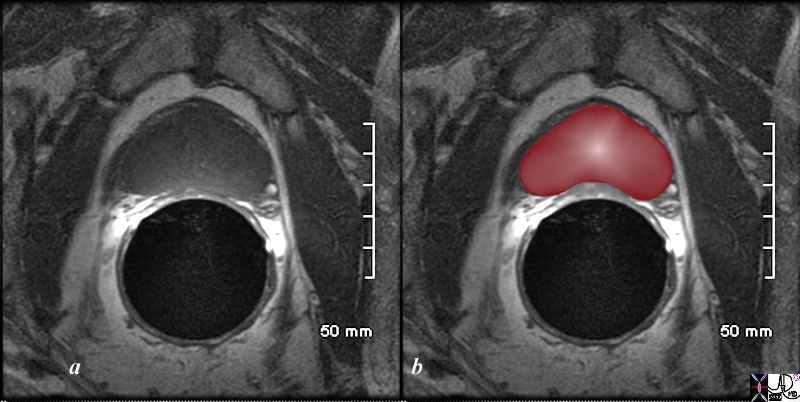
The patient is a 60 year old man. His MRI was performed with a transrectal coil and the image shows the T1 weighted sequence in the axial projection (a,b). The scan shown demonstrates the normal heart shape of the prostate at this level in the axial projection. Zonal anatomy cannot be distinguished on T1 sequences, since the T1 weighted sequence results in a homogenous signal from all the zones. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 98874cL.8s |
|
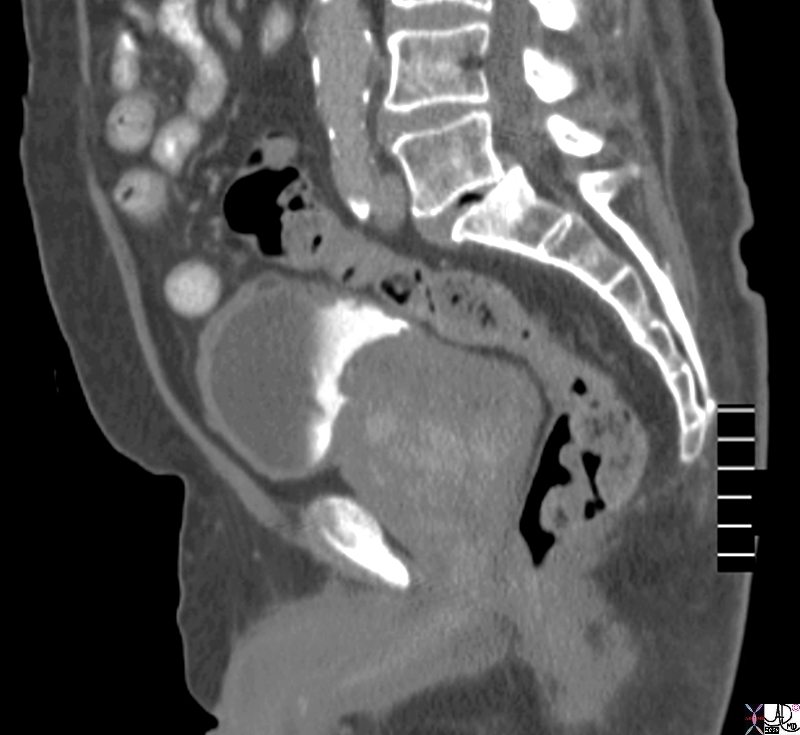
Large Smooth Gland in the Sagittal Plane |
|
The CTscan reconstructed in the sagittal plane is from a patient with an enlarged prostate. The borders become rounded best seen on the superior borders. The superior aspect of the gland protrudes with two symmetrical homogeneous components likely representing an enlarged transitional zone caused by hyperplasia. The matrix of the gland is heterogeneous The bladder wall is thickened anteriorly confirming outlet obstruction. Image Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 76771.8s |